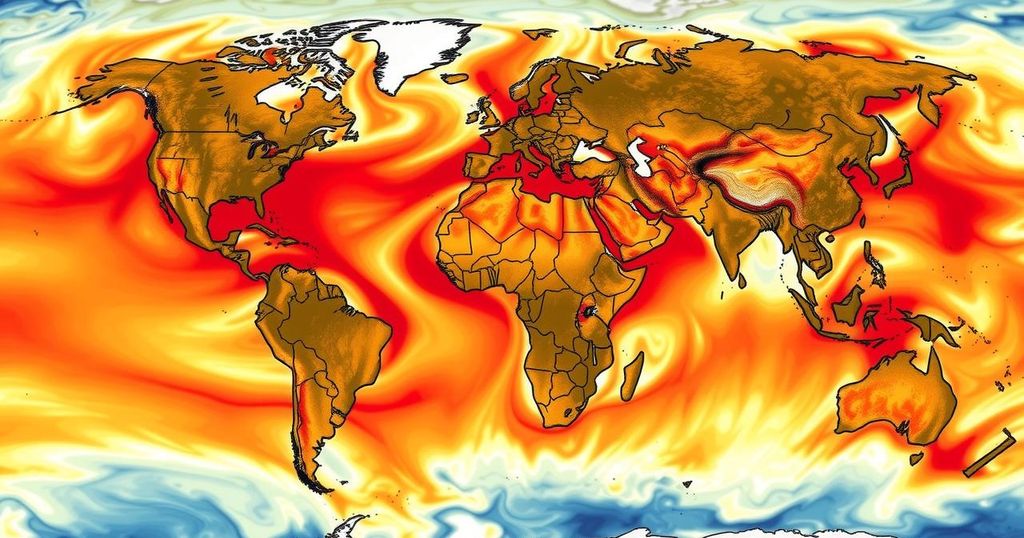
In 2024, the Earth experienced its warmest year on record, with temperatures 2.32°F above the 20th-century average. Antarctic sea ice coverage hit its second-lowest extent ever recorded. While ocean heat content was at an all-time high, global cyclone activity remained near average. These trends underscore the critical state of the planet’s climate and the urgent need for action against climate change.
In a recent analysis conducted by scientists at NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), it has been officially determined that 2024 was the warmest year recorded on the planet. Accompanying this unprecedented heat, Antarctic sea ice coverage has reached its second-lowest extent on record. This alarming trend continues a pattern established over the past decade, emphasizing the significant impacts of climate change.
The average land and ocean surface temperature for the year was noted to be 2.32 degrees Fahrenheit (1.29 degrees Celsius) above the 20th-century average, surpassing the previous record set in 2023 by 0.18 degrees Fahrenheit (0.10 degrees Celsius). Notably, all of the planet’s ten warmest years since 1850 have occurred within the last ten years, underscoring the urgency of addressing climate-related issues.
In addition to the temperature increase, notable declines in Antarctic sea ice coverage were recorded, peaking at 6.59 million square miles in September, which is also among the lowest recorded. Furthermore, the upper ocean heat content, a crucial climate indicator, reached its highest levels on record as the oceans continue to absorb 90% of excess heat in the Earth’s climate system.
Despite the increase in global temperatures, tropical cyclone activity in 2024 remained near the historical average, with 85 named storms recorded, a number closely aligned with the 1991–2020 averages. This indicates a complex relationship between global climate effects and extreme weather phenomena, necessitating continued vigilance and research.
The climate report issued by NOAA highlights significant concerns regarding global warming trends and changing climate patterns. The verification of 2024 as the warmest year on record draws attention to accelerated climate change and the resulting environmental consequences. With rising temperatures, ocean heat content is also a key metric in tracking climate change effects, revealing critical information about the planet’s environmental health. The systematic decline in polar ice coverage further illustrates the alarming impacts of global warming on Earth’s ecosystems.
The analysis from NOAA affirms that 2024 marked a pivotal moment in climate history, with unprecedented temperature levels and concerning declines in Antarctic sea ice. The data indicates that immediate action is required to address climate change and mitigate its drivers. Continued monitoring and research are essential to understanding these trends and fostering global awareness of climate-related issues.
Original Source: www.noaa.gov